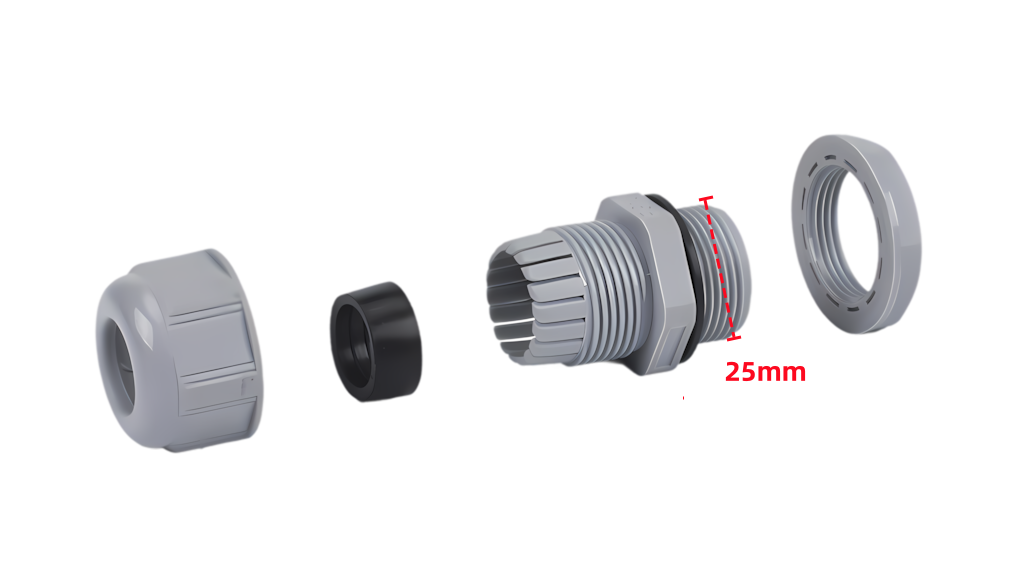
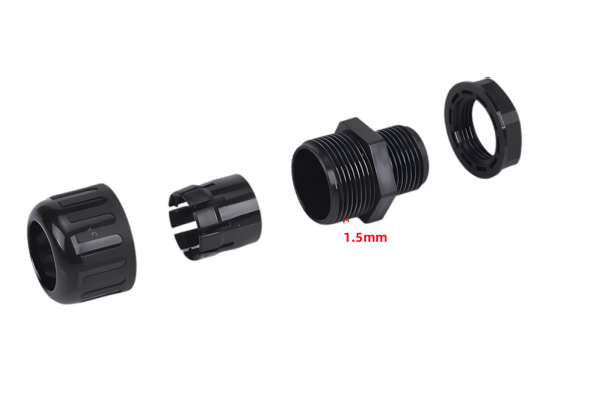
The joint M25×1.5 represents a kind of thread specification.
The specific meanings are as follows:
“M” indicates the metric thread.
“25” indicates that the major diameter of the thread is 25 millimeters.
“1.5” indicates that the pitch of the thread is 1.5 millimeters, that is, the axial distance between two corresponding points on the pitch diameter line of adjacent thread teeth is 1.5 millimeters.
Is a large thread pitch better or a small one better?
The size of the thread pitch (i.e., the pitch) has its own advantages and disadvantages. It cannot be simply said that a large pitch is better or a small pitch is better. It needs to be judged according to the specific application scenarios.
The specific meanings are as follows:
“M” indicates the metric thread.
“25” indicates that the major diameter of the thread is 25 millimeters.
“1.5” indicates that the pitch of the thread is 1.5 millimeters, that is, the axial distance between two corresponding points on the pitch diameter line of adjacent thread teeth is 1.5 millimeters.
Is a large thread pitch better or a small one better?
The size of the thread pitch (i.e., the pitch) has its own advantages and disadvantages. It cannot be simply said that a large pitch is better or a small pitch is better. It needs to be judged according to the specific application scenarios.
I. Characteristics and Advantages of a Large Pitch
- Quick Assembly and Disassembly
-
- A large pitch means that the thread advances a relatively large distance when it rotates one full turn. In some occasions where frequent installation and disassembly are required, such as in some temporarily built structures or equipment that needs to be adjusted frequently, it can save operation time and improve work efficiency.
-
- For example, in some temporary support structures on construction sites, using threaded connectors with a large pitch can enable quick construction and disassembly, which is convenient for construction.
-
- Relatively High Load-Bearing Capacity
-
- Generally, threads with a large pitch are usually designed to be thicker and stronger. This gives them a certain advantage when bearing a large axial force.
-
- For example, in some heavy machinery, such as the connecting parts of large cranes, high-strength threads with a large pitch may be used to ensure that they can bear huge loads.
-
II. Disadvantages of a Large Pitch
- Relatively Low Precision Requirements
-
- Due to the large pitch, the thread profile is relatively coarse, and the requirements for installation precision are relatively low. This is acceptable in some occasions where the precision requirements are not high, but in equipment that requires high-precision connection, it may lead to an insecure connection or loosening.
-
- For example, in precision instruments, threads with a small pitch can provide more precise adjustment and a tighter connection.
-
- Relatively Poor Self-Locking Performance
-
- The helix angle of threads with a large pitch is relatively large, and the self-locking performance is relatively poor. In some occasions with vibration or reverse force, it is easy to loosen, and additional anti-loosening measures need to be taken.
-
- For example, in parts with large vibrations such as automobile engines, threads with a small pitch are usually used, and anti-loosening washers and other measures are used in combination to ensure the reliability of the connection.
-
III. Characteristics and Advantages of a Small Pitch
- High Precision
-
- The thread profile of threads with a small pitch is relatively fine, and the requirements for installation precision are high. It can achieve more precise adjustment and a tighter connection.
-
- For example, in fields with extremely high precision requirements such as optical instruments and precision measuring equipment, threads with a small pitch can ensure the precise matching of various components and improve the performance and precision of the equipment.
-
- Good Self-Locking Performance
-
- The helix angle of threads with a small pitch is relatively small, and the self-locking performance is good. In some occasions where loosening needs to be prevented, such as in a vibration environment or under the action of a reverse force, threads with a small pitch can provide a more reliable connection.
-
- For example, in fields with extremely high safety requirements such as airplanes and spacecraft, threaded connections with a small pitch usually adopt special anti-loosening designs to ensure that they will not loosen under various extreme conditions.
-
IV. Disadvantages of a Small Pitch
- Slow Assembly and Disassembly Speed
-
- Since the thread with a small pitch advances a relatively small distance when it rotates one full turn, more rotations are required during installation and disassembly, and the operation is relatively slow.
-
- For example, in some mass production occasions, if threads with a small pitch are used, it may affect the production efficiency.
-
- Relatively Low Load-Bearing Capacity
-
- Threads with a small pitch usually have a relatively fine thread profile, and they may not be as good as threads with a large pitch when bearing a large axial force.
-
- For example, in some heavy-duty equipment, threads with a large pitch may be required to meet the load-bearing requirements.
-
